
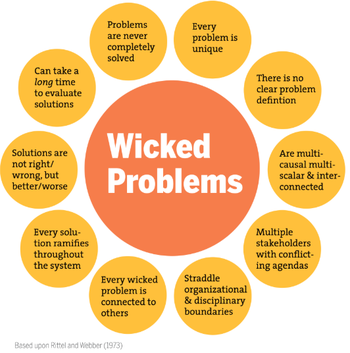
Sustaining anything as complex as the world and all its ecosystems and inhabitants is the most complex and profound of all ’wicked problems’(2) The Earth and all the systems of life it supports is complex. Left to its own devices it will, given sufficient time, adapt and regenerate regardless of the forces it is subject to. It might take millions of years but that is the time scale of planetary renewal.

Many of the resources we depend on are finite - when they are gone they will not be replenished. Natural and man-made disasters drive population movements on scales that destabilize societies. Human activity is changing the physical environment beyond all recognition and altering the climate in ways that will cause even more instability. The only thing that is certain is that we have created a future that is even less certain for our children and grandchildren. This state of being at the edge of chaos provides the context for our exploration of how we might use education as the means to educate a world into a more sustainable and more stable future.

Surely a task for LIfewide Education is to develop awareness and deeper understandings of this important issue so that we can begin to explore the ways in which concepts and practices of lifewide learning and ecological perspectives on learning and practice might contribute to the educational moral purpose of helping people sustain themselves through long and often disrupted learning lives, while protecting and sustaining the environment they inhabit for future generations.
Lifewide learning and education encourage a holistic approach to learning and personal development and view learning as an ecological phenomenon. They encourage learners to appreciate themselves as actors in and on the world, to appreciate the resources they draw upon and consume in order to learn and achieve the things they value, and to recognize and value the effects the world has on them. Understanding the ideas of ecology, development, sustainability and resilience in a fast changing and disruptive world are therefore key concepts for the lifewide learner and for educators and institutions who encourage and facilitate such learning.
(ESD) is commonly understood as education that encourages changes in knowledge, skills, values and attitudes to enable a more sustainable and just society for all. ESD aims to empower and equip current and future generations to meet their needs using a balanced and integrated approach to the economic, social and environmental dimensions of sustainable development (UNESCO).
This requires quality education and learning for sustainable development at all levels and in all social contexts including Higher Education. It means including key sustainable development issues and goals into teaching and learning practices. For example, learners should be made aware of such issues as poverty alleviation, peace, ethics, responsibility in local and global contexts, democracy and governance, justice, security, human rights, health, gender equity, cultural diversity, rural and urban development, economy, production and consumption patterns, corporate responsibility, environmental protection, natural resource management and biological and landscape diversity.
ESD means viewing our educational institutions and systems as living dynamic eco-social systems dedicated to the formation and development of knowledge and the encouragement and support of people's learning so that both individuals and the societal ecosystem as a whole cannot only be sustained but flourish.
ESD requires participatory teaching and learning methods that motivate and empower learners to change their behaviour and take action for sustainable development.
- Human sustainability in teaching: includes elements such as resilience, wellbeing, emotional intelligence and the role of personality and gender as a teacher
- Educational sustainability: comprehends open pedagogies, our legagy as a teacher, engagement with communities and society, and lifelong and lifewide learning (including digital capacity)
- Social and environmental education: gathers these issues within each ecological environment and with reference to our contribution to society as educators
Lifewide education encourages a more ecological approach to learning with the goal of enabling learners to develop themselves through all their experiences while at university so that they can sustain themselves through a lifetime of dealing with challenges and disruptions that they cannot begin to imagine8. Ultimately, universities have a moral responsibility to not just prepare learners for entry to the job market, they must enable learners to prepare themselves for the rest of their lives. Lifewide Education believes that adopting an educational approach that embraces the idea that a person’s learning and development is an ecological phenomenon involving themselves as whole creative beings interacting with their material and non-material world, provides a productive way of engaging with the ESD agenda. It aligns well with Daniel Wahl’s proposition(3):
‘It is time for designers — and all humans are designers to some extent — to think out of the box and assume responsibility of the effects or their actions’
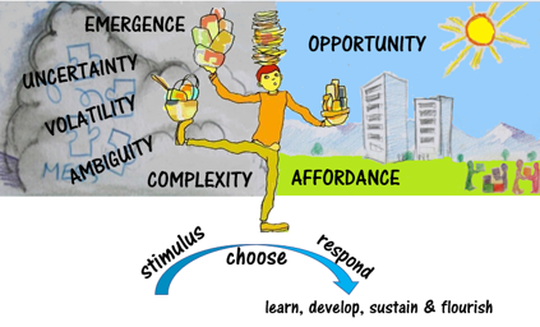
Stephen Covey gets to the heart of the matter through his habit of making particular and considered choices. ‘Between stimulus and response there is a space and in that space lies our freedom to choose our response. In those choices lie our growth and happiness.’(9) In the choices we make lie the means of sustaining ourselves and the world. The central proposition where sustainability is concerned is choosing to respond to a particular stimulus in a way that considers the wellbeing of others and future generations, not just our own wellbeing. At the heart of sustainability is a bigger purpose than ourselves. This is where education for sustainability plays an important part in informing the decisions we make about what we choose to do and what sort of person we chose to be. Lifewide Education argues that we can enhance our ability to respond by seeing our own practices as ecological deeply connected to the material and biological world and the people in it in ways that only we can see and appreciate, and which only emerge in the course of our actions.

We explore these ideas more thoroughly through a collection of writers and articles in Lifewide Magazine #20. You can join our exploration of what all this means for lifewide education by reading the magazine, sharing your views and experiences of supporting ESD and offering additional perspectives.
Norman Jackson
Commissioning Editor
1 World Commission on Environment and Development (1987) Our Common Future file:///C:/Users/norma/Downloads/our_common_futurebrundtlandreport1987.pdf
2 Rittel, H and Weber, M (1973) Dilemmas in a general theory of planning Policy Sciences Vol 4 155-169
3 Wahl, D,C. (2018) Introduction to the Worldview Dimension of Gaia Education’s course in ‘Design for Sustainability’ Age of Awareness https://medium.com/age-of-awareness/introduction-to-the-worldview-dimension-of-gaia-educations-course-in-design-for-sustainability-1577b7e4f460
4 UNESCO (2014) Shaping the Future We Want: UN Decade of Education for Sustainable Development (2005-2014) Final Report. Paris: UNESCO.
5 United Nations (2015) 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and its 17 Sustainable Development Goals. www.un.org/ sustainabledevelopment.
6 Leicht, A. Heiss, J. and Byun, W.J. (eds) (2018) Issues and trends in Education for Sustainable Development UNESCO Available at:
http://www.sustainabilityexchange.ac.uk/files/unesco_issues_and_trends_in_education_for_sustainable_development.pdf
7 PBL (2017) International Cooperation for the Sustainable Development Goals in 23 Infographics, PBL Nederlands Environmental Assessment Agency. Available at: http://www.sustainablesids.org/knowledgebase/pbl-people-and-the-earth-the-sdgs-in-23-infographics-2017
8 Jackson N J et al (eds) (2011) Learning for a Complex World: A lifwide concept of learning, education and development Authorhouse
9 Covey, S. R. (1989) The 7 Habits of Highly Effective People Simon and Shuster
10 Judson G (2018) Cultivating Ecological Understanding And Engagement With The World Through Imaginative Ecological Education (IEE) Lifewide Magazine #20
11 Jackson, N. J. (2011) An imaginative lifewide curriculum in N J Jackson et al (eds) Learning for a Complex World: A lifewide concept of learning education and development Authorhouse
Image credits
Diverse peoples cartoon artist Lai Meng-chia
http://www.taipeitimes.com/News/feat/photo/2016/07/01/2008135365
Wicked Problems Diagram Original source: CMU Transition Design, Irwin & Kossoff
https://medium.com/age-of-awareness/facing-complexity-wicked-design-problems-ee8c71618966
Children caring for the planet artist Ana-Karin Engberg taken from 'Children’s Voices about the State of the Earth and Sustainable Development' A report for the OMEP World Assembly and World Congress on the OMEP World Project on Education for Sustainable Development 2009-2010 July 2010
http://www.omep.org.se/uploads/files/congress_report_child_interviews_-_final.pdf


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
